From Alkenes
Catalytic Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation reactions that involve insoluble catalysts ⇒ heterogeneous catalysis. (, , ) Hydrogenation reactions that involve soluble catalysts ⇒ homogeneous catalysis. ( - Wilkinson’s catalyst.)
Unsaturated compounds can be reduced to saturated compounds by catalytic hydrogenation.
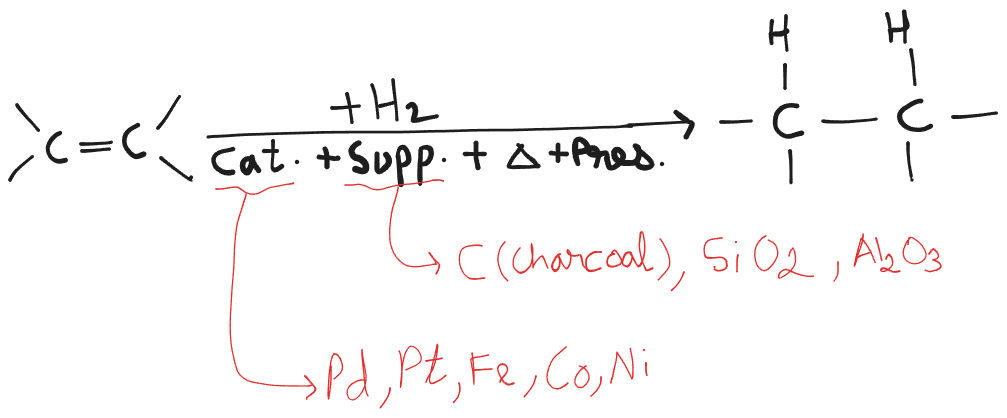
- Support is used to prevent the catalyst from destroying its catalytic activity.
Refer:
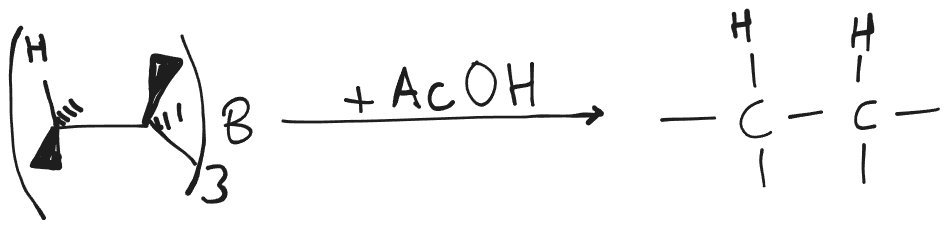
Hydroboration Reduction or Dimerisation
- Syn-addition.
- Boron is added to that carbon which is less sterically hindered.
Refer:
Reduction
Dimerisation
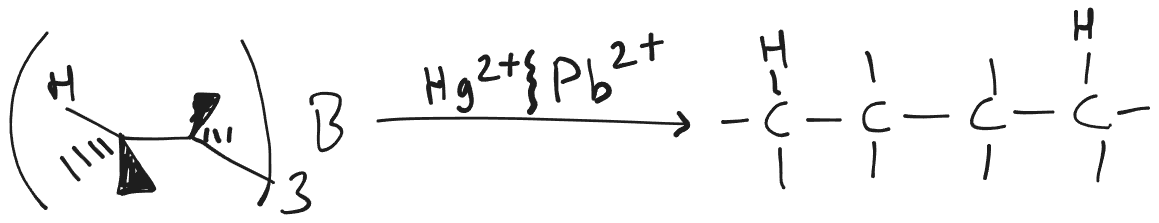
From Alkynes
Catalytic Hydrogenation takes place twice.
From Alkyl Halides
Wurtz Reaction
Formation of higher alkanes from alkyl halides in the presence of sodium and dry ether is named Wurtz reaction. It can proceed with ionic as well as radical mechanisms.
Disproportionation products can also be formed. Cyclic products can also be formed.
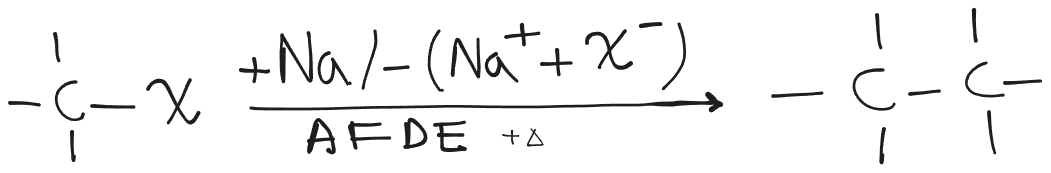
If the substrate is tertiary, addition reaction is not preferred due to the bulky nature (steric hindrance.) Instead, the disproportionation reaction becomes exclusive.
Corey-Posner Whitesides-House Synthesis
Refer to Corey-Posner, Whitesides-House Synthesis.
Reduction with Metal Hydride
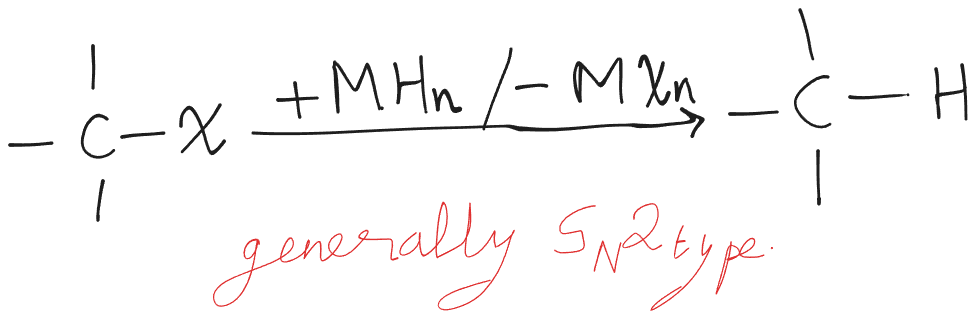
| Metal Hydride | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LAH / | Y | Alkene | Alkene |
| / | N | Y | Y |
| / | Y | Y | Y |
- Y → acts as a nucleophile and substitution takes place.
- Alkene → acts as a base and elimination might take place.
- N → No reaction.
LAH → provides in higher concentrations, so for reactive substances it starts acting as a base. → Due to the high covalent nature of bonds, reactions fail to take place for primary alkylhalides.
Refer to:
Reduction with Metal Acid
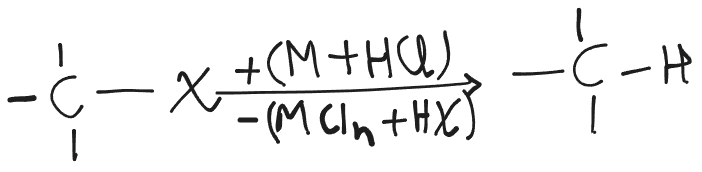
Reduction with Zinc Alcohol
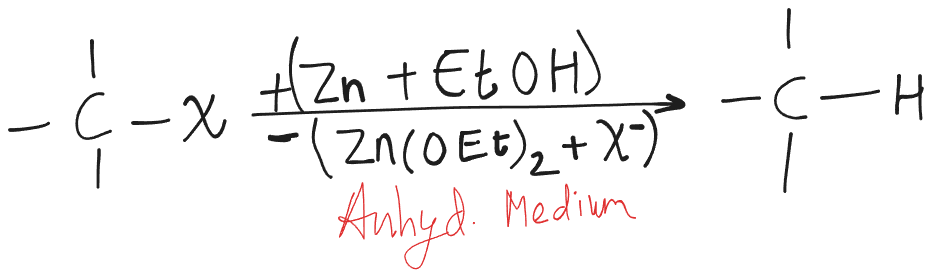
is more stable than .
From Alcohols
It is not possible to synthesize alkanes from alcohols.
From Carbonyl Compounds
Clemmensen Reduction
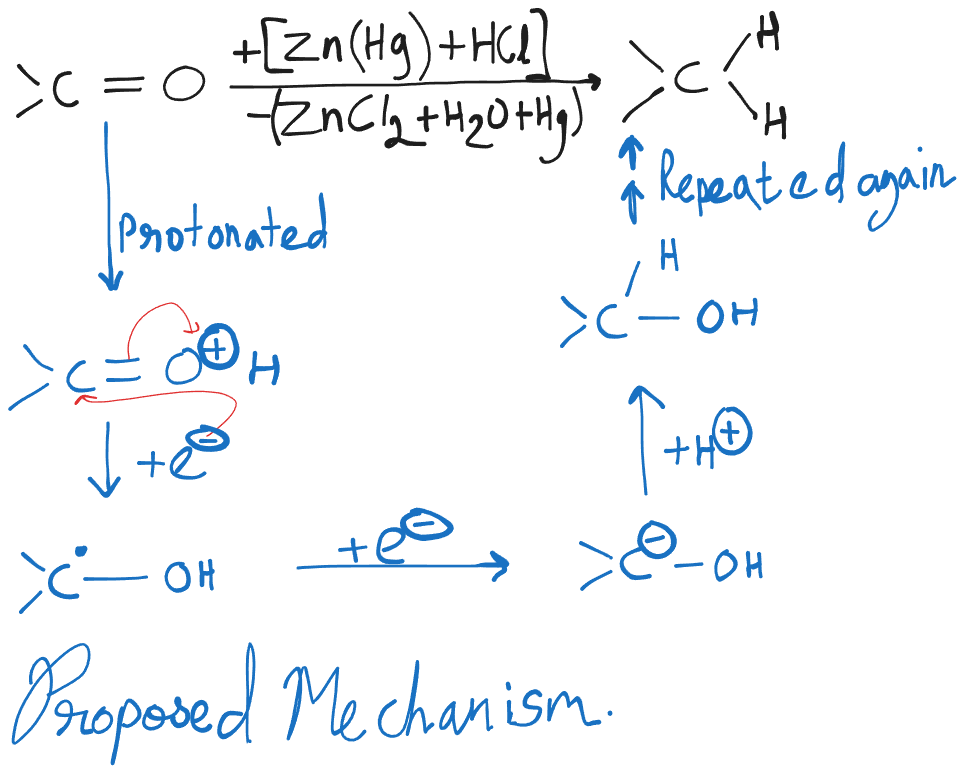
This reaction is not effective for those substrates which contain acid-sensitive groups. Zinc and Hydrochloric acid also reduces nitro groups to amino groups.
Wolff-Kishner Reduction
It can be thought to complement Clemmensen Reduction as that occurs under acidic condition, while this in basic.
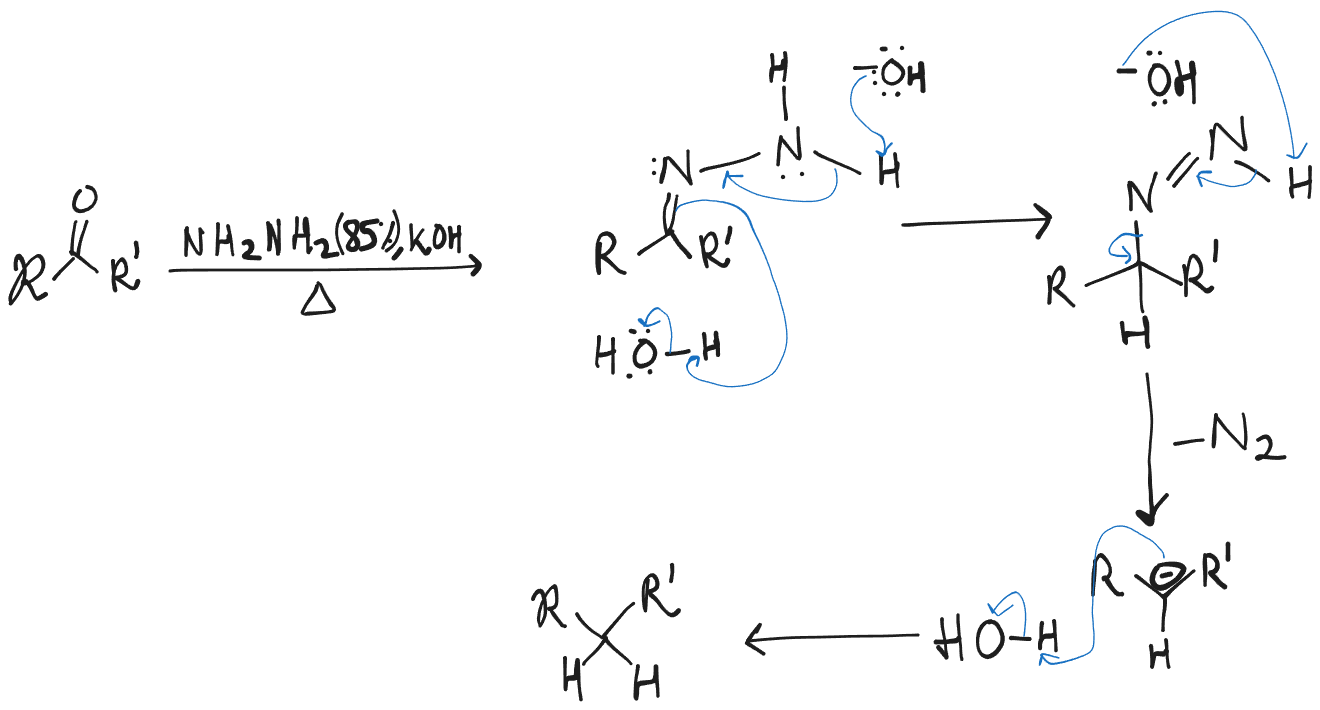
Note that the hydrogen is not from the base, nor from the hydrazine but rather from the solvent, (in this case ). Another solvent that commonly is used is Ethylene Glycol ().
Mozingo Reduction
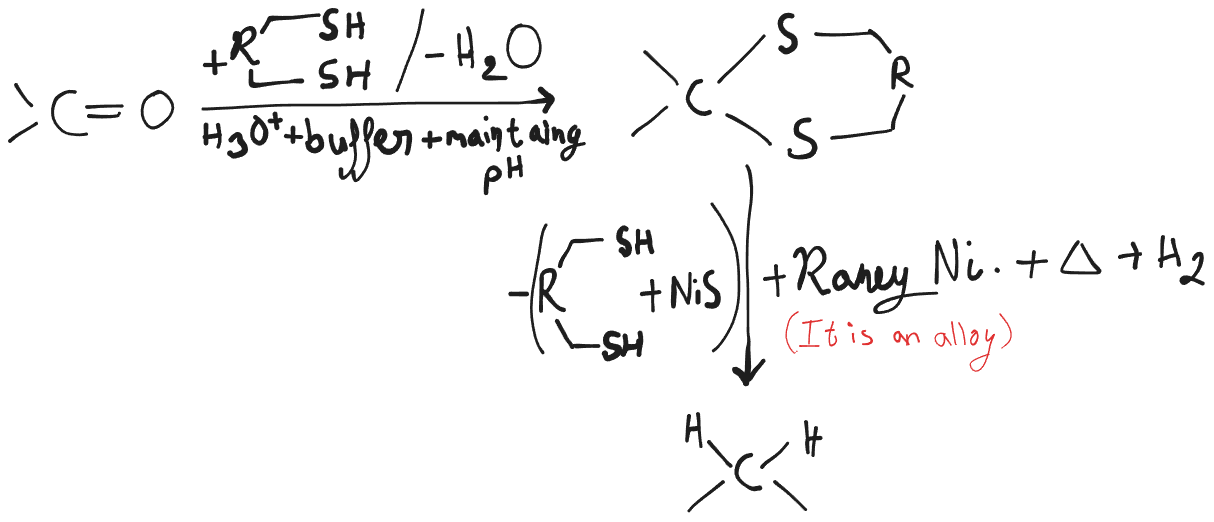
Desulfurization with Hydrogen and Raney Nickel.